Working from home—at least in part—is the new normal for many employees. This presents new challenges for IT organizations as they seek to ensure cybersecurity approaches can effectively secure remote work.
In this blog series, I’m sharing how you can adjust your cybersecurity strategy to meet the requirements of a remote and/or hybrid workforce, where employees use personal devices and cloud services outside the corporate network.
Putting yourself in the users’ workflows and understanding what they need to accomplish their jobs will be the foundation of your ability to deploy a modern work approach and implement Zero Trust as part of your modernization effort.
How the Zero Trust Model Mitigates Challenges in Remote and Hybrid Work Cybersecurity
For SMB technology leaders, transitioning from traditional network controls to a Zero Trust model is crucial for modern security because the way employees work today is drastically different from the way they worked when most traditional infrastructure and approaches were developed.
Traditional methods rely on firewalls and VPNs, trusting user accounts and devices by default. In contrast, Zero Trust combines policies, processes, and technology to verify user identities and devices continuously, regardless of location. This approach ensures robust security from cloud to edge, protecting your network, data, and applications whether employees are in the office, at home, or on the go.
The adoption cycle for securing remote and hybrid work
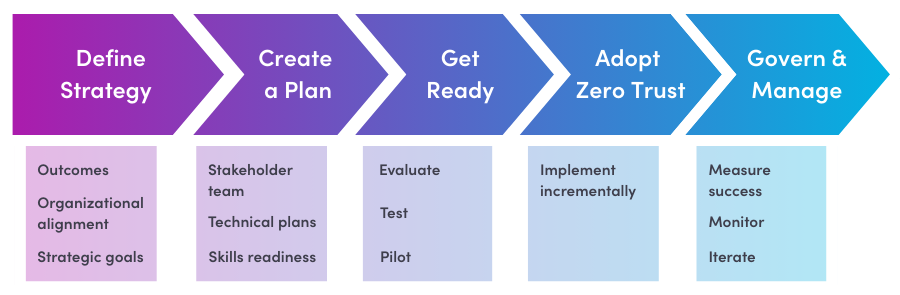
Securing remote and hybrid work with Zero Trust requires implementing basic yet advanced security measures. This involves policy enforcement and monitoring for all access to your organization’s resources using a full end-to-end lifecycle approach.
This article discusses this business scenario through the phases of the Cloud Adoption Framework for Azure, adapted for Zero Trust:
- Define Strategy: Specify successful outcomes & align the organization
- Create a Plan: Identify stakeholders, create technical plans, and understand required skills
- Get Ready: Evaluate current standing and test your plan
- Adopt Zero Trust: Implement your strategy across your environment and organization.
- Govern and Manage: Monitor your environment and iterate for continuous improvement.
In this first blog, we’ll dive into the first two stages of the Zero Trust Adoption Cycle: Define Strategy and Create a Plan.

Stage 1: Defining Your Strategy for Secure Remote Work
The Define Strategy phase is essential for articulating and formalizing our approach to addressing the underlying reasons for this scenario. During this phase, we examine the scenario from business, IT, operational, and strategic perspectives.
We specify the outcomes to measure success within the scenario, recognizing that security is a progressive and iterative process.
Examples of Motivations and Outcomes to Define Your Strategy
Securing remote and hybrid work is essential, but different parts of the organization have various incentives. The following table highlights these motivations:
| Business Needs | Provide secure access to information anytime, anywhere on any device, managing data access risks without compromising security. |
| IT Needs | Standardize identity platforms for both human and non-human identities, eliminate VPN needs, and manage corporate and BYOD devices remotely while ensuring a seamless user experience. |
| Operational Needs | Standardize existing security solutions, lower management effort for secure identities, and improve identity governance by managing user access effectively. |
| Strategic Needs | Standardize existing security solutions, lower management effort for secure identities, and improve identity governance by effectively managing user access. |
Strategies for Implementing Zero Trust to Secure Remote Work
To be productive, users must be able to use:
- Their user account credentials to verify their identity.
- Their endpoint (device), such as a PC, tablet, or phone.
- The applications you have provided to them.
- The data required to perform their job.
Understanding how they use these components as part of their role becomes a cornerstone of your approach. To help break this down, you can look at the network over which traffic flows between devices and applications, whether the user and their device are on-premises or on the internet.
Attackers target each one of these elements and must be protected according to the Zero Trust principle: “never trust, always verify.”
| Productivity | Organizations aim to extend productivity securely to users and their devices without limiting employee capabilities based on workforce location. |
| Safe Access | Company data and applications need to be accessed by authorized employees securely to protect company intellectual property and personal data. |
| Support End Users | As organizations adopt a hybrid workforce approach, employees require additional application and platform capabilities for a secure and mobile work experience. |
| Increase Security | The security of current or proposed work solutions needs enhancement to help organizations adapt to mobile workforce requirements. Security capabilities should match or exceed those available to the on-premises workforce. |
| Empower IT | The IT team focuses on securing the workplace starting with the employee’s user experience, without significantly increasing friction for users. Additionally, the IT team requires processes and visibility for governance and the ability to detect and mitigate cyberattacks. |
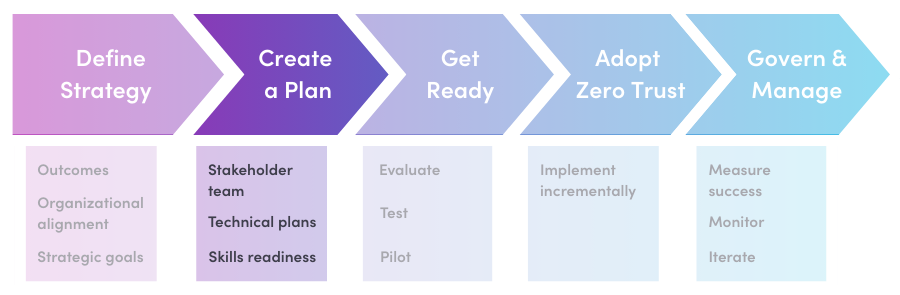
Stage 2: Create a Plan
Adoption plans transform the aspirational goals of a Zero Trust strategy into a practical framework. These plans provide technical teams with guidance on how to align their efforts with the organization’s business objectives.
The defined motivations and outcomes, developed in collaboration with business leaders and teams, articulate the rationale behind the strategy. They serve as the guiding principles, or North Star, for executing the strategy. The later step involves detailed technical planning to achieve these objectives.
The following exercises are intended to assist in implementing your organization’s technology strategy. They support Zero Trust adoption initiatives by identifying and prioritizing essential tasks. Upon completing this process, you will have a thorough cloud adoption plan that aligns with the metrics and motivations outlined in the cloud adoption strategy.

Implementing security for remote and hybrid work environments requires a phased strategy to enforce Zero Trust principles across identities, devices, and applications. This includes the following requirements:
- Multifactor authentication (MFA) with Conditional Access must be applied to all user identities accessing the environment.
- Devices should be enrolled in device management systems and continuously monitored for health status.
- Access to applications and their data should require verification of identities, healthy devices, and proper data access permissions.
Organizations can achieve these deployment objectives by adopting a four-stage approach, as outlined in the following chart:
Some additional resources from Microsoft you can use as part of your approach include a downloadable PowerPoint slide deck to present and report on your progress through these stages and objectives to business leaders and other stakeholders. Here’s the slide for this business scenario.
Additionally, you can use this Excel workbook to assign owners and track your progress for these stages, objectives, and tasks.
If your organization follows a particular Governance Risk & Compliance (GRC) or Security Operations Center (SOC) strategy, it is essential that the technical work includes configurations that fulfill these requirements.
Understand your organization
Each organization’s needs and composition are different. A multinational enterprise with multiple applications and standardized security will implement security differently from a startup or a medium-sized organization.
Regardless of the size and complexity of your organization, consider these actions:
- Inventory users, endpoints, apps, data, and networks to assess security status and estimate the effort needed to transform the estate.
- Document goals and plan for incremental adoption based on priorities. For instance, start by securing identities and Microsoft 365 services, followed by endpoints. Then, secure apps and SaaS services using modern authentication methods and segmentation capabilities provided by Conditional Access.
- For the principle of least privileged access, inventory accounts with privileged access and reduce them to the minimum necessary. Accounts requiring privileged access should use just-in-time and just-enough-access (JIT/JEA) to limit standing administration privileges. In case of a breach, compromised accounts are limited, minimizing the impact. Except for a “break glass” account, standing admin access should not be allowed for highly privileged roles, including application administration roles for productivity services like SharePoint, Exchange, and Teams.
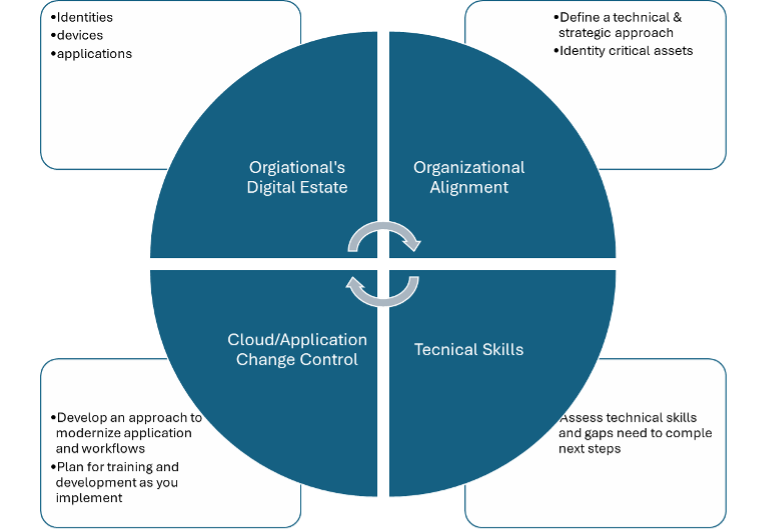
Organizational planning and alignment
The implementation and governance of a secure access methodology affects several overlapping areas and is typically implemented in the order of:
- Identities
- Endpoints (devices)
- Apps
- Network
Protecting data is also essential for securing remote and hybrid work. This topic is addressed more thoroughly in Identify and protect sensitive business data.
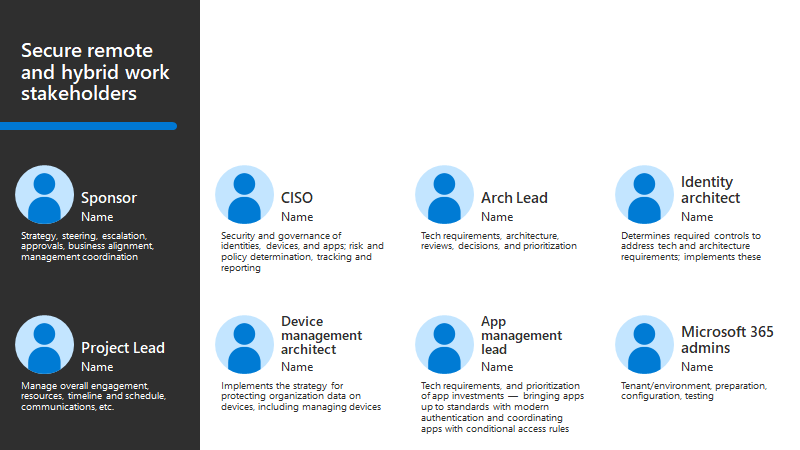
Do not forget to take into consideration the needs of the various stakeholders, see the image below:
Robust data protection is essential for remote and hybrid work models. This requires a systematic deployment process, divided into four crucial stages that address specific objectives and resources. Following these stages helps safeguard sensitive business data and optimize work environments. Let’s explore how these stages contribute to a secure and efficient deployment.

Cloud adoption plan
A Zero Trust adoption plan is essential for transitioning to an advanced security strategy that includes change management and governance. It covers securing identities, endpoints, apps, and networks, both existing and new. Planning for remote and hybrid work involves protecting current identities and creating new ones that meet security standards.
Training staff is crucial:
- Train administrators on new privileged access methods to reduce friction.
- Equip Helpdesk and IT personnel with a clear security message that balances attacker friction with secure working benefits.
- Create user adoption materials to ensure an understanding of security as a shared responsibility aligned with business goals.
For more information from the Cloud Adoption Framework, see the Plan for cloud adoption.

;)