As organizations accelerate their digital transformation, automation is no longer a luxury; it is a necessity. While tools like ARM and Bicep have redefined infrastructure as code in Azure, there remains a critical need for a flexible, extensible scripting engine that can unify automation across the Microsoft and wider ecosystems. This is where PowerShell excels.
Why PowerShell?
PowerShell has grown far beyond its origins as a Windows administration tool. Today, PowerShell runs almost anywhere and integrates with nearly every major cloud and enterprise platform. PowerShell combines a powerful scripting language with a command-line shell, enabling IT professionals and developers to automate repetitive tasks, orchestrate complex workflows, and manage resources across Windows, Linux, and macOS environments.
For organizations moving toward automation maturity, PowerShell provides an easy-to-learn platform that allows teams to solve problems quickly from an interactive console, while also having the capabilities required to automate even the most complex systems and workflows.
Practical Applications
PowerShell’s versatility is its greatest strength. Here are some of the most impactful ways organizations are leveraging PowerShell for automation:
- Infrastructure Management: Automate provisioning, configuration, and monitoring of servers, virtual machines, and cloud resources. PowerShell modules for Azure, Microsoft 365, and Active Directory enable unified management from a single interface.
- User Lifecycle Automation: Streamline onboarding, offboarding, and access management by integrating PowerShell scripts with identity platforms and HR systems. You can read about how we accomplish this in Enhancing Microsoft Identity: Quisitive User Lifecycle Management
- Security and Compliance: Enforce policies, audit configurations, and remediate vulnerabilities at scale. PowerShell’s ability to interact with APIs and security tools makes it indispensable for security professionals.
- DevOps and CI/CD: Integrate PowerShell into build and release pipelines for automated testing, deployment, and environment validation. PowerShell’s compatibility with Azure DevOps and GitHub Actions supports robust DevOps practices.
- Endpoint Management: Automate software deployment, patching, and configuration across fleets of devices, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors.
Integration Strategies: PowerShell as the Essential IaC Companion
While declarative IaC tools like ARM, Bicep, and Terraform excel at defining and provisioning infrastructure, they often fall short when it comes to the nuanced, procedural tasks that real-world deployments demand. PowerShell bridges these gaps, enabling organizations to achieve true end-to-end automation.
Where PowerShell Complements IaC Solutions:
Environment Preparation:
IaC templates can provision resources, but preparing an environment often requires additional steps, such as setting up network rules, initializing storage, or configuring prerequisites. PowerShell scripts can orchestrate these tasks before, during, or after template deployment, ensuring environments are truly ready for workloads.
Provisioning App Registrations and Identity Resources:
Bicep, and Terraform can create Entra ID (Azure AD) resources, but complex scenarios, like registering applications, assigning permissions, or integrating with external identity providers, often require API calls or conditional logic. PowerShell, with its robust support for Microsoft Graph and REST APIs, automates these advanced identity tasks seamlessly.
Orchestrating Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Workflows:
PowerShell’s cross-platform capabilities allow it to automate tasks across Azure, on-premises, and even other clouds, something that’s challenging for most IaC tools. This makes PowerShell invaluable for organizations with hybrid or multi-cloud strategies.
Post-Deployment Customizations:
After infrastructure is provisioned, organizations frequently need to:
- Copy data between storage accounts or databases
- Install or configure applications on VMs
- Apply custom security policies or compliance settings
- Trigger notifications or integrate with ticketing systems
These actions typically fall outside the scope of declarative templates. PowerShell scripts can be invoked as part of deployment pipelines or runbooks to handle these customizations, ensuring that environments are not just provisioned, but fully operational and tailored to business needs.
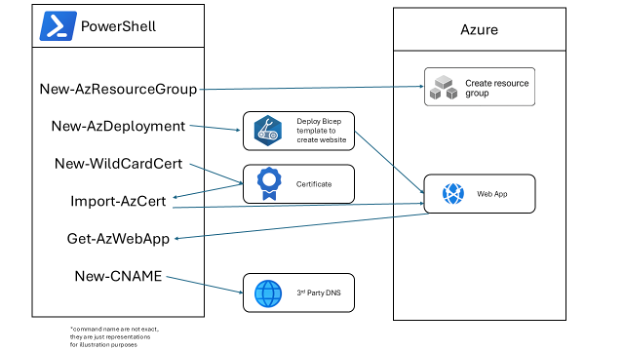
PowerShell is the automation glue that binds IaC solutions together, filling the gaps left by declarative tools and enabling organizations to automate smarter, not just faster.
PowerShell Integration Strategies
PowerShell’s true power emerges when it is integrated with other Microsoft automation tools:
- With Azure Automation/Functions: Author reusable runbooks in PowerShell to automate cloud and on-premises operations, schedule recurring tasks, and respond to events.
- With Microsoft Graph and REST APIs: Extend automation beyond native modules by interacting with virtually any service that exposes an API, including third-party platforms.
- With DevOps Pipelines: Embed PowerShell scripts in CI/CD workflows to automate testing, compliance checks, and environment setup.
Quisitive Insight: PowerShell as the Automation Glue
At Quisitive, PowerShell is a cornerstone of our automation practice. For example, our Managed Automation team uses PowerShell with our Cloud Automation Platform (CAP) to orchestrate complex workflows that span Azure, Microsoft 365, and on-premises environments, enabling rapid, repeatable deployments and proactive monitoring.
We use PowerShell to drive our user lifecycle automation for enterprise clients, resulting in measurable gains in efficiency and compliance. In one engagement, PowerShell scripts automated the onboarding and offboarding of users, reducing manual effort by over a dozen FTEs and ensuring consistent application of security policies.
PowerShell is more than a scripting language, it is the automation glue that binds multiple ecosystems together to achieve true end-to-end automation, driving scalability, consistency, and agility across environments.
Real-World Example: PowerShell for Log4j Vulnerability Identification
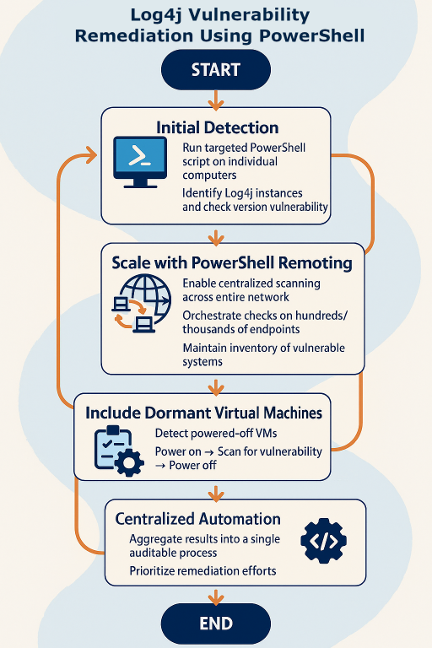
A few years back when the Log4j vulnerability surfaced, our team leveraged PowerShell to rapidly identify and remediate risks across the entire environments. The process began with a targeted PowerShell script designed to search individual computers for instances of Log4j and determine if they were running vulnerable versions. This initial approach provided immediate visibility into affected assets and enabled quick action at the machine level.
Recognizing the need for scale, we evolved our solution by utilizing PowerShell remoting. This allowed us to scan entire networks with a single click, orchestrating vulnerability checks across hundreds or thousands of Windows and Linux servers simultaneously. PowerShell’s ability to centralize and automate these scans meant that we could maintain a comprehensive inventory of vulnerable systems and prioritize remediation efforts efficiently.
To ensure no asset was overlooked, we extended our automation to include virtual machines that were powered off. PowerShell was used to identify these dormant VMs, power them on, perform the vulnerability scan, and then return them to their previous state. This closed a critical gap, ensuring that even inactive systems were assessed and secured.
The result was a centralized, repeatable, and auditable process for vulnerability management. PowerShell not only enabled the discovery of Log4j vulnerabilities but also provided the orchestration needed for a coordinated response. By combining PowerShell’s procedural automation with existing infrastructure-as-code practices, we achieved both defined infrastructure and operational assurance.
These scripts then became another tool in our belt and can now be used in any situation where we need to access every server at the drop of a hat, securely and safely.
You can see for yourself how we checked all Windows and Linux Azure VMs, as well as on-premises systems, with a single script: AzureVM-Log4j.ps1
Getting Started with PowerShell
For those new to PowerShell, the learning curve is approachable. Start by exploring the basics—cmdlets, pipelines, and scripting fundamentals. Microsoft and LinkedIn Learning offer comprehensive courses for all skill levels, from introductory overviews to advanced automation scenarios.
You can also explore my YouTube channel or check out my weekly PowerShell newsletter for more educational resources.
To maximize the value of PowerShell:
- Adopt a modular approach: Write reusable functions and scripts to promote consistency and simplify maintenance.
- Leverage community resources: The PowerShell Gallery and GitHub host thousands of modules and scripts for common automation tasks.
- Integrate with CI/CD: Use PowerShell in your DevOps pipelines to automate testing and deployments.
- Prioritize security: Follow best practices for script signing, credential management, and least privilege.
Closing Thoughts
PowerShell remains an essential tool for any organization seeking to automate smarter. Its flexibility, extensibility, and deep integration with Microsoft platforms make it uniquely positioned to address the challenges of modern IT operations. As you advance your automation journey, consider how PowerShell can unify your workflows and unlock new possibilities for efficiency and innovation.
Make sure to check out the other blogs in this series:
- Part 1: Automate Smarter: Microsoft Tools You Should be Using Right Now
- Part 2: Democratizing Automation with Microsoft’s Power Platform
- Part 3: ARM & Bicep – Modern Infrastructure as Code for Azure
- Part 4: PowerShell for Automation (This Article)
Coming Soon:
- Part 5: Azure functions
- Part 6: Azure Automation
- Part 7: Quisitive’s Cloud Automation Platform
- Part 8: Automation and Agentic AI

;)



